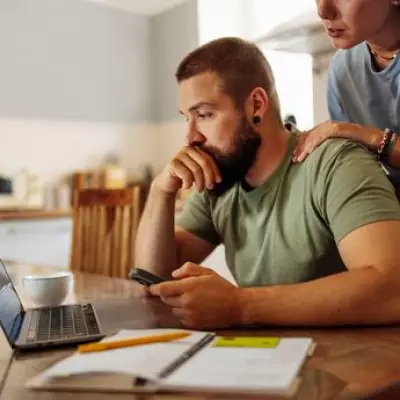
Health experts are sounding the alarm over a hazardous new trend among users of popular weight loss injections. The practice, known as microdosing, involves taking smaller, more frequent doses of medication to make expensive injection pens last longer.
The Dangers of Reusing Needles
Jason Murphy, Head of Pharmacy and weight loss expert at Chemist4U, has highlighted needle reuse as one of the most serious problems arising from this trend. He explains that taking smaller doses necessitates more injections, which multiplies the health risks if a fresh needle is not used every single time.
Once a needle pierces the skin, its tip becomes blunt. This can make subsequent injections more painful and lead to bruising, swelling, and soreness. Over time, this can cause lasting tissue inflammation, making future injections far more difficult and painful to administer.
Bacterial Contamination and Treatment Disruption
A used needle can also become partially blocked by residual medication, disrupting the delivery of the dose. This interference can lead to unpredictable effects, stall progress, or make side effects harder to manage.
The most critical risk, however, is bacterial contamination. "Even a single reuse of a needle can lead to harmful bacteria build-up directly under your skin," Murphy warned. "This increases the risk of painful infections, redness, swelling, and can even require medical attention." As needles are not sterile after use, each injection with a reused needle creates a direct pathway for bacteria to enter the body.
Long-Term Tissue Damage and Ineffective Dosing
Beyond infection, repeated injections in the same area can cause a condition called lipohypertrophy. This is a build-up of lumpy, scarred tissue under the skin which can:
- Interfere with how efficiently the body absorbs medication.
- Create hardened patches that make injections more difficult.
Experts stress that using fresh needles and carefully rotating injection sites is crucial to prevent this and other complications.
Murphy also cautioned that deviating from the prescribed dose could worsen side effects and carry unknown risks. Small variations in dose from microdosing can have a disproportionate impact on the treatment's effectiveness and safety. He advises patients to always read the instructions carefully and stick to the recommended dosage to ensure the best possible results.
With limited scientific evidence supporting the benefits of microdosing, health professionals are urging the public to follow medical guidance and avoid this dangerous cost-cutting practice.